Master Coconut Oil Processing: From Pretreatment to Refining
- Type: coconut oil processing plant
- Usage/Application: coconut, copra
- Raw material: Rhizome
- Supply type: OEM/ODM
- Product Aroma: 8 types
- Feature: Skin Revitalizer, Moisturizing, Anti-aging, Firming
- Ingredient: Rose
- Country: botswana
Coconut oil processing plant. Explore the world of coconut oil production with Huatai's advanced facilities, designed for high efficiency and maximum yield. Our video highlights our capacity to process vast quantities of coconut oil, from 30 to 1000 TPD, and our sophisticated solvent extraction techniques that ensure every drop of oil is captured.
Coconut Oil Manufacturing Plant, Costs | Setup Report 2025
- Type: coconut oil processing machine
- Production capacity: 20-2000TPD
- Voltage: 380V
- Weight: standard
- Dimension (L*W*H): standard
- Power (W): Standard
Coconut Oil Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025 Edition. Report Coverage: Industry Analysis (Market Performance, Segments, Price Analysis, Outlook), Detailed Process Flow (Product Overview, Unit Operations, Raw Materials, Quality Assurance), Requirements and Cost (Machinery, Raw Materials, Packaging, Transportation, Utility, Human Resource), Project Economics (Capital Investments
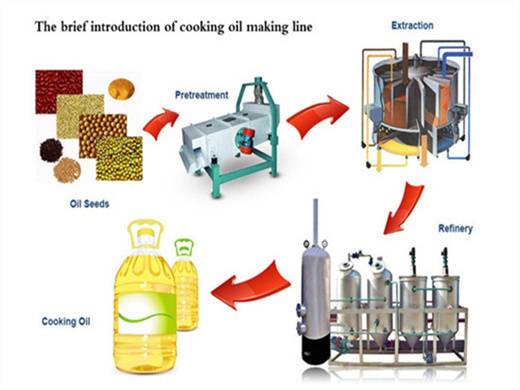
Coconut oil plant adopts twice pressing technology to produce coconut oil from the dried copra. The coconut oil production line mainly includes copra pretreatment and oil pressing process, oil refining process. Copra cake produced after pressing can be used as animal feed. We provide 30-1000 TPD coconut oil processing machine and 1-600 TPD
Coconut Processing Plant Report 2025: Setup & Cost - IMARC Group
- Usage: coconut oil
- Voltage: 220V/380V/410V
- Power: 2.2KW
- Certification: ISO9001
- Weight: Based on refined oil cooking machine Capacity
- Dimension (L *W*H): 1910*550*765 mm
IMARC Group’s report, titled “Coconut Processing Plant Project Report 2025: Industry Trends, Plant Setup, Machinery, Raw Materials, Investment Opportunities, Cost and Revenue” provides a complete roadmap for setting up a coconut processing plant. It covers a comprehensive market overview to micro-level information such as unit operations
Processing methods of virgin coconut oil include disintegration of coconut kernel, extraction of milk, and separation of oil from water using a high-speed tubular type centrifuge followed by filtration and packing. Desiccated coconut powder, is a rich source of fat & protein.
Virgin Coconut Oil Processing Plant | Coconut Oil Processing
- Type: cooking oil extraction machine
- Production capacity: 1-1000TPD
- Power ( W): 5.5 kW
- Voltage: 220V/380V
- Dimension (L*W*H): 1.5*2.6*3.6 M
- Weight: 30 tons
Virgin Coconut Oil Processing Plant Coconut oil, extracted from fresh coconut meat, distinguishes itself from copra-derived oils. Utilizing quick-drying or wet-milling methods, our machines employ mechanical pressing for the initial extraction, followed by a meticulous process involving boiling, fermentation, refrigeration, enzymes, or
They also use virgin coconut oil machinery. They use a high-speed centrifuge to segregate the virgin coconut oil from raw coconut milk. In the fermentation method, they keep the coconut milk for 24 hours to ferment it. The process is natural, and the virgin coconut oil floats on the top. Then they will scoop out this layer of the oil and filter it.
Comprehensive Guide to Coconut Processing Technology: From
- Raw Material: coconut
- Production capacity: 40-600 kg/h
- Dimension (length x width x height). ): 390*150*280mm
- Voltage: 220 V
- Weight: 6.5 KG
- Main components: Motor, PLC, Others, Gears
Coconut processing starts with harvesting and ends with making products. We’ll cover the key steps in coconut processing. These include harvesting, dehusking, deshelling, and drying. These steps are crucial for making many coconut products. Coconut processing methods change based on the product needed. But most involve drying, grinding, or
2. Coconut Oil Extraction. Coconut oil extraction is another important process in the coconut oil processing plant. To extract oil for making use of chemical solvent to dissolve oil content contained in cake or direct oil seeds, just for lower oil seeds, as an example soybean. Then oil is separated from solvent by vaporizing solvent out.